If you’ve read about electric vehicles in the news lately, you know the vibes are bad. Over the past few weeks, the media has fixated on the idea that consumer demand for EVs is “slowing,” “chilling,” or “losing its charge.”
But are sales even slowing? Has federal policy failed to spark the EV transition? Is there any cause for panic? The data shows none of that is true.
The best (and only) quantitative evidence presented for the dominant media narrative is data from Cox Automotive, as presented in a recent Wall Street Journal article, showing that dealers are taking more time and resorting to bigger discounts to move EVs off their lots.That’s true, but does it really indicate that EV sales are “slowing”?
First, this data excludes the space’s biggest player by far — Tesla — as well as other EV-only makers like Rivian who don’t use dealer networks, so this is really a story about traditional automakers (Ford, GM, Volkswagen, etc). And with high interest rates making a new car more costly to finance or lease, dealer discounts are trending steadily upwards for all vehicles in recent months, not just electric models, according to the Cox data.
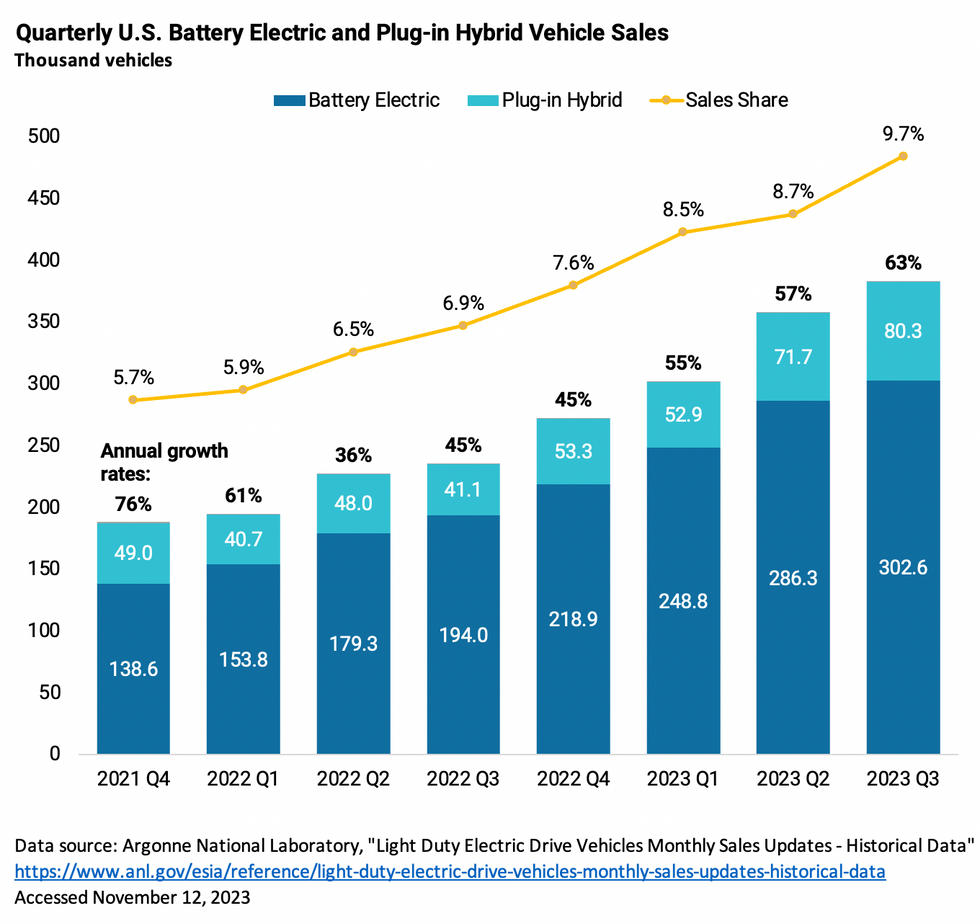
Second, if we take a look at actual sales data, there’s no sign the growth in EVs is flagging. In fact, sales of battery electric and plug-in hybrid vehicles in the third quarter of 2023 exhibited the strongest year-on-year growth since the fourth quarter of 2021.

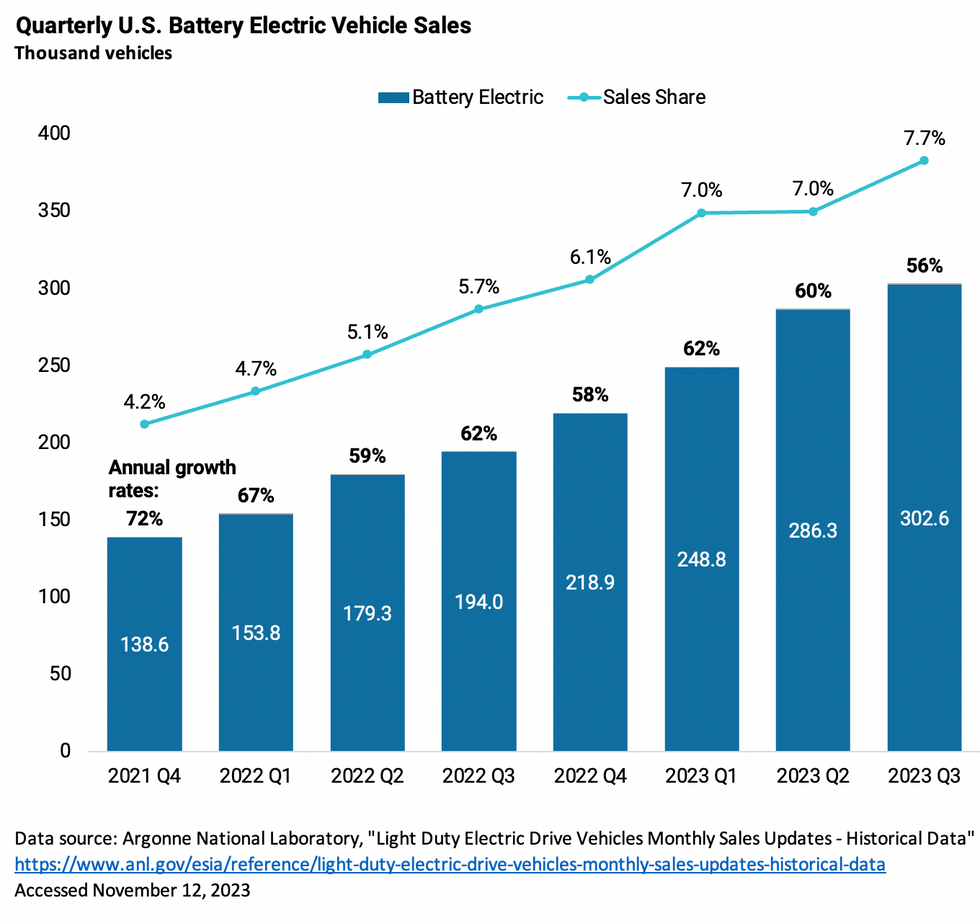
Putting aside plug-in hybrids, which have shorter electric range and retain a gasoline engine, sales of purely electric vehicles have been steadily increasing at a roughly 60 percent annual growth rate for each of the last six quarters. That’s fast enough to double EV sales every 14 months!

Overall, year-to-date sales of electric and plug-in hybrid vehicles in the U.S. topped 1 million in September for the first time and are on pace to exceed 1.4 million by year’s end.It’s hard to square the actual data with the bad vibes.
The main story here is not of cooling consumer interest in EVs or a slow-down of the electric transition, but rather the confluence of two other major factors — Tesla’s defensive price war and rising interest rates — which have forced some incumbents to rethink their strategies.
For most of the last decade, Tesla has basically had the EV market to itself. As a result, they priced even their mass-market models, the Model 3 and Model Y, as if they were in competition with Audis and BMWs not Corollas or CRVs. Tesla’s long head start also gave them ample time to bring down manufacturing costs. High price points and falling production costs sent Tesla’s profit margin soaring to a peak of nearly 30% in March 2022, compared to the single digit margins more typical of a high-volume auto manufacturer.
Then, as soon as traditional automakers got serious about the EV business and new start-ups like Rivian and Lucid started scaling, Tesla aggressively slashed prices. The base Model 3 cost over $48,000 last year. Today, it costs around $38,000, a 20% drop. Prices for the Model Y have fallen by a similar magnitude.
Yes, price cuts have eaten into Tesla profitability, but they appear to be an effective defensive weapon that hit their rivals at exactly the same time the Fed was ratcheting up interest rates, substantially increasing the cost of financing or leasing any new vehicle.
In 2021 and 2022, as traditional automakers were launching new flagship EVs, it seemed like they could easily sell every EV they could produce at premium-prices, all while dealers charged big markups.
But just as the market was flooded with new electric offerings, high interest rates made buyers more cost conscious and Tesla’s price cuts took all the fat out of the market. The EV market of 2023 is cutthroat, and aggressive pricing is king.
These shifting market realities seem to have caught several legacy automakers off guard and forced a major refocus on reducing cost of production.
Indeed, if we dive into the data, it’s clear that the ominous headlines about the “slowing” EV market are more a story about Ford and GM in particular, than anything else.
Sales of Ford’s Mach-E have indeed flatlined this year, likely due to competition from Tesla’s now-discounted Model Y. Noting that reducing sticker price on electric vehicles would be their top priority, Ford CEO Jim Farley recently announced adjustments to F-150 Lightning and Mach-E production ramps and delayed some capital spending.
GM’s EV ambitions are stuck in neutral too, but their woes can hardly be attributed to a lack of customer interest. The company is struggling with serious difficulties assembling the Ultium batteries meant to power their next generation of electric SUVs and pickups. As a result, GM shipped only 2,316 of their Cadillac Lyriq crossover and 65 electric GMC Hummers in the first half of this year, a slower pace than 2022. Less than 200 of their Chevy Blazer and Silverado EVs found their way to American homes through September. Amidst these production troubles, GM pushed back the launch of the Chevy Equinox EV and full-scale production of their electric pickups by several months. Meanwhile, sales of the one EV they do have on the market, the affordable Chevy Bolt, are going gangbusters. Unfortunately, GM plans to stop producing the Bolt by year’s end as it focuses on modernizing the venerable model.
(Stellantis, the parent company of Chrysler, Jeep and Ram, has yet to launch any all-electric vehicles in the United States, though their plug-in hybrid Jeeps are selling strongly this year).
Still, contrary to recent headlines, none of the major automakers are scrapping plans for huge investments in electric vehicles. Fresh details on the recent deals struck between the UAW and the Big Three (GM, Ford, and Stellantis) show the automakers all continue to plan multi-billion-dollar investments in new EV factories and models.
“Our commitment to an all-EV future is as strong as ever,” GM CEO Mary Barra told analysts on a conference call last month. The company plans to be 100% electric by 2035.
Ford is “not moving away from our second generation [EV] products,” the company’s CFO also said in October.
Meanwhile, Hyundai Motor Group (parent to Hyundai, Kia, and Genesis brands) continues to launch new electric models and its executives told investors the company isn’t pausing EV plans as they “believe EV sales will grow longer term.” In fact, the Korean auto group vaulted ahead of GM and Ford to snag the #2 spot for total U.S. EV sales this year.
Volvo’s electric sales more than doubled over the past year to reach 13% of total sales for the brand, and the company reported a healthy 9% profit margin on its electric models.
Upstart Rivian is going strong too. Sales of its R1 series tripled over the last year, and the firm just increased its 2023 production estimates by 4 percent to 54,000 vehicles as it continues to move towards profitability with a focus on reducing costs and ramping up production.
The upshot of all this is that EVs are getting more affordable, which is the key to future growth. Prices are falling. Dealer markups are gone. And the price of an average EV in September was $50,683 (before tax credits), barely higher than the average for all new vehicles ($48,000).
In January, the personal EV tax credit will be available to buyers at the point of sale for the first time too, effectively turning it into a rebate. Already, intense competition is forcing dealers to pass the credit through as a down payment that cuts the monthly cost of leasing a $40,000 EV nearly in half.
Next year will also see the more affordable Volvo EX30 and Chevy Equinox EV hit the market, joining the Tesla Model 3, Hyundai Kona, and Kia Niro and Ioniq 6 in the under $40k segment.
In 2024, Tesla’s extensive Supercharger network will also open up to non-Teslas, virtually all automakers will adopt NACS chargers natively in model year 2025 vehicles and beyond, and the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law’s National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure grants will finally start to flow in earnest to build out chargers.
So while Ford and GM are facing real challenges, the overall state of the electric vehicle market is healthy.
As GM’s Barra said: “As we get further into the transformation to EV, it's a bit bumpy.” But that doesnt mean the journey is slowing. Sales of EVs keep growing rapidly, new models are expanding the market, and competition is making it all more affordable. Doesn’t that deserve some good vibes for a change?










 Pfluger in the U.S. Capitol. Photo by Andrew Harnik/Getty Images
Pfluger in the U.S. Capitol. Photo by Andrew Harnik/Getty Images
