Abstract
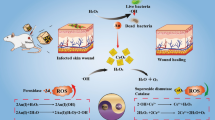
Lysosome-targetable selenium-doped carbon nanodots (Lyso-Se-CDs) that can efficiently scavenge lysosomal •OH in living cells and mice were designed in this research. Se-CDs with redox-responsive fluorescence (λex = 379 nm, λem = 471 nm, quantum yield = 7.1%) were initially synthesized from selenocystine by a facile hydrothermal method, followed by the surface modification with morpholine, a lysosome targeting moiety. The as-synthesized Lyso-Se-CDs exhibited excellent colloidal stability, efficient scavenging abilities towards •OH, low biotoxicity, as well as good biocompatibility and lysosome targetability. Due to these desirable properties, Lyso-Se-CDs had been successfully utilized for rescuing cells from elevated lysosomal •OH levels. More importantly, Lyso-Se-CDs efficiently relieved phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) triggered ear inflammation in live mice. These findings reveal that Lyso-Se-CDs are potent candidates for treating •OH-related inflammation.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hou J-T, Yu K-K, Sunwoo K, Kim WY, Koo S, Wang J, Ren WX, Wang S, Yu X-Q, Kim JS (2020) Fluorescent imaging of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species associated with pathophysiological processes. Chem 6:832–866
Li H, Ma H (2018) New progress in spectroscopic probes for reactive oxygen species. J Anal Test 2:2–19
Zhen X, Pu K (2018) Development of optical nanoprobes for molecular imaging of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. Nano Res 11:5258–5280
Huang H, Tian Y (2018) A ratiometric fluorescent probe for bioimaging and biosensing of HBrO in mitochondria upon oxidative stress. Chem Commun 54:12198–12201
Liu Z, Tian Y (2021) Recent advances in development of devices and probes for sensing and imaging in the brain. Sci China Chem. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426
Kowaltowski AJ, De Souza-Pinto NC, Castilho RF, Vercesi AE (2009) Mitochondria and reactive oxygen species. Free Radic Biol Med 47:333–343
Valko M, Izakovic M, Mazur M, Rhodes CJ, Telser J (2004) Role of oxygen radicals in DNA damage and cancer incidence. Mol Cell Biochem 266:37–56
Valko M, Leibfritz D, Moncol J, Cronin MTD, Mazur M, Telser J (2007) Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 39:44–84
Markesbery WR, Carney JM (1999) Oxidative alterations in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Pathol 9:133
Kwon HJ, Cha M-Y, Kim D, Kim DK, Soh M, Shin K, Hyeon T, Mook-Jung I (2016) Mitochondria-targeting ceria nanoparticles as antioxidants for Alzheimer’s disease. ACS Nano 10:2860–2870
Kwon HJ, Kim D, Seo K, Kim YG, Han SI, Kang T, Soh M, Hyeon T (2018) Ceria nanoparticle systems for selective scavenging of mitochondrial, intracellular, and extracellular reactive oxygen species in Parkinson's disease. Angew Chem Int Ed 57:9408–9412
Yao J, Cheng Y, Zhou M, Zhao S, Lin S, Wang X, Wu J, Li S, Wei H (2018) ROS scavenging Mn3O4 nanozymes for in vivo anti-inflammation. Chem Sci 9:2927–2933
Bao X, Zhao J, Sun J, Hu M, Yang X (2018) Polydopamine nanoparticles as efficient scavengers for reactive oxygen species in periodontal disease. ACS Nano 12:8882–8892
Liu T, Xiao B, Xiang F, Tan J, Chen Z, Zhang X, Wu C, Mao Z, Luo G, Chen X, Deng J (2020) Ultrasmall copper-based nanoparticles for reactive oxygen species scavenging and alleviation of inflammation related diseases. Nat Comomun 11:2788
Li H, Cao X, Fei X, Zhang S, Xian Y (2019) Nanoscaled luminescent terbium metal–organic frameworks for measuring and scavenging reactive oxygen species in living cells. J Mater Chem B 7:3027–3033
Huang Y, Liu C, Pu F, Liu Z, Ren J, Qu X (2017) A GO-Se nanocomposite as an antioxidant nanozyme for cytoprotection. Chem Commun 53:3082–3085
Liu Y, Cheng Y, Zhang H, Zhou M, Yu Y, Lin S, Jiang B, Zhao X, Miao L, Wei C-W, Liu Q, Lin Y-W, Du Y, Butch CJ, Wei H (2020) Integrated cascade nanozyme catalyzes in vivo ROS scavenging for anti-inflammatory therapy. Sci Adv 6:eabb2695
Wu H, Li F, Wang S, Lu J, Li J, Du Y, Sun X, Chen X, Gao J, Ling D (2018) Ceria nanocrystals decorated mesoporous silica nanoparticle based ROS-scavenging tissue adhesive for highly efficient regenerative wound healing. Biomaterials 151:66–77
Wu Y, Huang W, Peng D, Huang X-A, Gu J, Wu S, Deng T, Liu F (2021) Synthesis of dihydroquinolines as scaffolds for fluorescence sensing of hydroxyl radical. Org Lett 23:135–139
Benitez-Martin C, Guadix JA, Pearson JR, Najera F, Perez-Pomares JM, Perez-Inestrosa E (2019) A turn-on two-photon fluorescent probe for detecting lysosomal hydroxyl radicals in living cells. Sensors Actuators B Chem 284:744–750
Li F, Yang D, Xu H (2019) Non-metal-heteroatom-doped carbon dots: synthesis and properties. Chem Eur J 25:1165–1176
Zhou J, Zhou H, Tang J, Deng S, Yan F, Li W, Qu M (2017) Carbon dots doped with heteroatoms for fluorescent bioimaging: a review. Microchim Acta 184:343–368
Zhou D, Huang H, Wang Y, Wang Y, Hu Z, Li X (2019) A yellow-emissive carbon nanodot-based ratiometric fluorescent nanosensor for visualization of exogenous and endogenous hydroxyl radicals in the mitochondria of live cells. J Mater Chem B 7:3737–3744
Liu Z, Pei H, Zhang L, Tian Y (2018) Mitochondria-targeted DNA nanoprobe for real-time imaging and simultaneous quantification of Ca2+ and pH in neurons. ACS Nano 12:12357–12368
Li F, Li T, Sun C, Xia J, Jiao Y, Xu H (2017) Selenium-doped carbon quantum dots for free-radical scavenging. Angew Chem Int Ed 56:9910–9914
Rosenkrans ZT, Sun T, Jiang D, Chen W, Barnhart TE, Zhang Z, Ferreira CA, Wang X, Engle JW, Huang P, Cai W (2020) Selenium-doped carbon quantum dots act as broad-spectrum antioxidants for acute kidney injury management. Adv Sci 7:2000420
Su R, Shi J, Pu Y, Wang J-X, Wang D, Chen J-F (2020) Synthesis of ultrasmall and monodisperse selenium-doped carbon dots from amino acids for free radical scavenging. Ind Eng Chem Res 59:16876–16883
Zhu J-H, Feng Y-G, Wang A-J, Mei L-P, Luo X, Feng J-J (2021) A signal-on photoelectrochemical aptasensor for chloramphenicol assay based on 3D self-supporting AgI/Ag/BiOI Z-scheme heterojunction arrays. Biosens Bioelectron 181:113158
Shen Z, Cai Q, Yin C, Xia Q, Cheng J, Li X, Wang Y (2020) Facile synthesis of silica nanosheets with hierarchical pore structure and their amine-functionalized composite for enhanced CO2 capture. Chem Eng Sci 217:115528
Luo W, Wang Y, Lin F, Liu Y, Gu R, Liu W, Xiao C (2020) Selenium-doped carbon quantum dots efficiently ameliorate secondary spinal cord injury via scavenging reactive oxygen species. Int J Nanomedicine 15:10113–10125
Ye X, Xiang Y, Wang Q, Li Z, Liu Z (2019) A red emissive two-photon fluorescence probe based on carbon dots for intracellular pH detection. Small 15:1901673
Huang H, Shen Z, Chen B, Wang X, Xia Q, Ge Z, Wang Y, Li X (2020) Selenium-doped two-photon fluorescent carbon nanodots for in-situ free radical scavenging in mitochondria. J Colloid Interface Sci 567:402–409
Simões EFC, Leitão JMM, Esteves Da Silva JCG (2017) Sulfur and nitrogen co-doped carbon dots sensors for nitric oxide fluorescence quantification. Anal Chim Acta 960:117–122
Bauer C, Jacques P, Kalt A (1999) Investigation of the interaction between a sulfonated azo dye (AO7) and a TiO2 surface. Chem Phys Lett 307:397–406
Wang Y, Hu A (2014) Carbon quantum dots: synthesis, properties and applications. J Mater Chem C 2:6921
Li H, He X, Kang Z, Huang H, Liu Y, Liu J, Lian S, Tsang CHA, Yang X, Lee ST (2010) Water-soluble fluorescent carbon quantum dots and photocatalyst design. Angew Chem 122:4532–4536
Lu S, Sui L, Liu J, Zhu S, Chen A, Jin M, Yang B (2017) Near-infrared photoluminescent polymer–carbon nanodots with two-photon fluorescence. Adv Mater 29:1603443
Dam BV, Nie H, Ju B, Marino E, Paulusse JMJ, Schall P, Li M, Dohnalová K (2017) Excitation-dependent photoluminescence from single-carbon dots. Small 13:1702098
Liu H, Sun Y, Li Z, Yang J, Aryee AA, Qu L, Du D, Lin Y (2019) Lysosome-targeted carbon dots for ratiometric imaging of formaldehyde in living cells. Nanoscale 11:8458–8463
Wang Q, Zhou L, Qiu L, Lu D, Wu Y, Zhang X-B (2015) An efficient ratiometric fluorescent probe for tracking dynamic changes in lysosomal pH. Analyst 140:5563–5569
Huang H, Lou X, Hu B, Zhou Z, Chen J, Tian Y (2019) A comprehensive study on the generation of reactive oxygen species in Cu-Aβ-catalyzed redox processes. Free Radic Biol Med 135:125–131
Wu J, Yu Y, Cheng Y, Cheng C, Zhang Y, Jiang B, Zhao X, Miao L, Wei H (2021) Ligand-dependent activity engineering of glutathione peroxidase-mimicking MIL-47(V) metal–organic framework nanozyme for therapy. Angew Chem Int Ed 60:1227–1234
Funding
The authors gratefully thank the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. LQ20B050003) and Grant from the Scientific Research Start-up Project Foundation of Jiaxing University (CD70519012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Nanomaterials for biomedical imaging and targeting
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 2128 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, D., Huang, H., Yu, J. et al. Lysosome-targetable selenium-doped carbon nanodots for in situ scavenging free radicals in living cells and mice. Microchim Acta 188, 223 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04883-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04883-1