Abstract
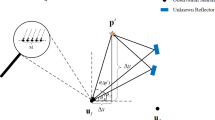
In this paper, we propose a novel sparse time difference of arrival (S-TDOA) estimation method for the localization of the low probability of intercept (LPI) signals using distributed sensors. The proposed method uses the phase linearity of the wideband spatial covariances between the sensors obtained using sparse data. In the conventional distributed sensor systems, whole the data between the sensors is required to be transmitted to a central processor with a high computational load. In this work, the TDOA estimation is performed by using sparse sensor data in order to reduce computational load and high data sharing rate, which is more desirable for the practical implementations. It is shown in various simulations that the proposed method can effectively estimate the TDOA between the distributed sensors using the sparse multi-sensor data even in low signal-to-noise ratio. It is also shown that the TDOA estimation performance of the proposed method follows to Cramer Rao lower bound. Moreover, it is also shown that the data sharing rate and computation time are quite reduced without a significant performance loss with the sparsity process.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akansu, A. N., Duhamel, P., Lin, X., & De Courville, M. (1998). Orthogonal transmultiplexers in communication: A review. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 46(4), 979–995.
Pickholtz, R., Schilling, D., & Milstein, L. (1982). Theory of spread-spectrum communications-a tutorial. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 30(5), 855–884.
Chamola, V., Kotesh, P., Agarwal, A., Gupta, N., & Guizani, M. et al.(2020). A comprehensive review of unmanned aerial vehicle attacks and neutralization techniques. Ad Hoc Networks, p 102324.
Wang, J., Liu, Y., & Song, H. (2021). Counter-unmanned aircraft system (s)(c-uas): State of the art, challenges, and future trends. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 36(3), 4–29.
Farrell, T. C., & Prescott, G.(1996) A low probability of intercept signal detection receiver using quadrature mirror filter bank trees. In 1996 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing Conference Proceedings, vol 3, pp 1558–1561. IEEE.
Wiley, R. G.(2006) ELINT: The interception and analysis of radar signals. Artech House
Zhang, H., Wei, P., & Mou, Q. (2013). A semidefinite relaxation approach to blind despreading of long-code DS-SS signal with carrier frequency offset. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 20(7), 705–708.
Vankayalapati, N., & Kay, S. (2012). Asymptotically optimal detection of low probability of intercept signals using distributed sensors. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 48(1), 737–748.
Pace, P. E.(2009) Detecting and classifying low probability of intercept radar. Artech House.
Wymeersch, H., Lien, J., & Win, M. Z. (2009). Cooperative localization in wireless networks. Proceedings of the IEEE, 97(2), 427–450.
Rappaport, T. S., Reed, J. H., & Woerner, B. D. (1996). Position location using wireless communications on highways of the future. IEEE Communications Magazine, 34(10), 33–41.
Li, W., & Jia, Y. (2015). Distributed target tracking by time of arrival and received signal strength with unknown path loss exponent. IET Signal Processing, 9(9), 681–686.
Chenguang, S., Jianjiang, Z., & Fei, W. (2016). Lpi based resource management for target tracking in distributed radar network. In 2016 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), pp 1–5. IEEE.
Shen, J., Molisch, A. F., & Salmi, J. (2012). Accurate passive location estimation using toa measurements. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 11(6), 2182–2192.
Wang, G., Cai, S., Li, Y., & Jin, M. (2013). Second-order cone relaxation for toa-based source localization with unknown start transmission time. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 63(6), 2973–2977.
Gezici, S. (2008). A survey on wireless position estimation. Wireless Personal Communications, 44(3), 263–282.
Wang, G., & Chen, H. (2011). An importance sampling method for tdoa-based source localization. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 10(5), 1560–1568.
Bin, X., Sun, G., Ran, Yu., & Yang, Z. (2013). High-accuracy tdoa-based localization without time synchronization. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 24(8), 1567–1576.
Huang, B., Xie, L., & Yang, Z. (2014). Tdoa-based source localization with distance-dependent noises. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 14(1), 468–480.
Li, W., Tang, Q., Huang, C., Ren, C., & Li, Y. (2017). A new close form location algorithm with aoa and tdoa for mobile user. Wireless Personal Communications, 97(2), 3061–3080.
Lee, K., Jungkeun, O., & You, K. (2017). Closed-form solution of tdoa-based geolocation and tracking: A recursive weighted least square approach. Wireless Personal Communications, 94(4), 3451–3464.
Kim, S.-D., & Chong, J.-W. (2017). A novel tdoa-based localization algorithm using asynchronous base stations. Wireless Personal Communications, 96(2), 2341–2349.
Wang, G., So, A.M.-C., & Li, Y. (2016). Robust convex approximation methods for tdoa-based localization under nlos conditions. IEEE Transactions on Signal processing, 64(13), 3281–3296.
Uysal, C., Filik, T. (2014). Presence detection of long-and-short-code DS-SS signals using the phase linearity of multichannel sensors. In 19th International Conference on Digital Signal Processing (DSP), 2014, pp. 305–309.
Uysal, C., Filik, T. (2015). A joint detection and localization method for non-cooperative DS-SS signals. In Military Communications Conference, MILCOM 2015–2015 IEEE, pp. 523–528.
Uysal,C., Filik, T. (2016). The localization of lpi signals using sparse tdoa estimates. In 2016 24th Signal Processing and Communication Application Conference (SIU), pp. 1669–1672.
Naresh, V. & Steven, K. (2010). Asymptotically optimal detection/localization of LPI signals of emitters using distributed sensors. In SPIE Defense, Security, and Sensing, pp 77060U–77060U.
Hamschin, B., Clancy, J., Grabbe, M., Fortier, M., & Novak, J. (2014). Passive detection, characterization, and localization of multiple LFMCW LPI signals. In 2014 IEEE Radar Conference, pp. 0537–0543.
Denk, A. (2006). Detection and jamming low probability of intercept (LPI) radars. DTIC Document: Technical report.
Jiang, L., Li, L., & Zhao, G. Q. (2016). Polyphase coded low probability of intercept signals detection and estimation using time-frequency rate distribution. IET Signal Processing, 10(1), 46–54.
Kishore, T. R., & Deergha, R. K. (2017). Automatic intrapulse modulation classification of advanced lpi radar waveforms. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 53(2), 901–914.
Kong, S.-H., Kim, M., Hoang, L. M., & Kim, E. (2018). Automatic lpi radar waveform recognition using cnn. IEEE Access, 6, 4207–4219.
Shi, C., Wang, F., Salous, S., & Zhou, J. (2018). Low probability of intercept-based optimal ofdm waveform design strategy for an integrated radar and communications system. IEEE Access, 6, 57689–57699.
Knapp, C., & Clifford Carter, G. (1976). The generalized correlation method for estimation of time delay. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, 24(4), 320–327.
Clifford Carter, G., Nuttall, A. H., & Cable, P. G. (1973). The smoothed coherence transform. Proceedings of the IEEE, 61(10), 1497–1498.
Hannan, E. J., & Thomson, P. J. (1973). Estimating group delay. Biometrika, 60(2), 241–253.
So, H. C., Chan, Y. T., & Chan, F. K. W. (2008). Closed-form formulae for time-difference-of-arrival estimation. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 56(6), 2614–2620.
Chan, Y.-T., & Ho, K. C. (2005). Joint time-scale and tdoa estimation: Analysis and fast approximation. IEEE Transactions on Signal processing, 53(8), 2625–2634.
Guo, F., Zhang, Z., & Yang, L. (2016). TDOA/FDOA estimation method based on dechirp. IET Signal Processing, 10(5), 486–492.
Piersol, A. (1981). Time delay estimation using phase data. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, 29(3), 471–477.
So, H. C. (2001). Time-delay estimation for sinusoidal signals. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 148(6), 318–324.
Huang, Y., Lin, J., & M, G. (2013). High accuracy time delay measurements for band-pass signals. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 62(11), 2998–3005.
Chan, Y. T., Hattin, R., & Plant, J. B. (1978). The least squares estimation of time delay and its use in signal detection. In IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, ICASSP ’78.,3, 665–669.
Ahnström, U., Falk, J., Händel, P., Wikström, M. (2003). Detection and direction-finding of spread spectrum signals using correlation and narrowband interference rejection. In Nordic Matlab Conference. COMSOL A/S.
Falk, J., Händel, P., Jansson, M. (2002). Direction finding for electronic warfare systems using the phase of the cross spectral density. In RadioVetenskap och Kommunikation (RVK), Stockholm, Sweden, June 2002, pp. 264–268.
Pages-Zamora, A., & Vidal, J. (2002). Closed-form solution for positioning based on angle of arrival measurements. In The 13th IEEE International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications,4(4), 1522–1526.
Sathish, C. (2005). Advances in Direction-of-arrival Estimation. Artech House.
FaIk, J., Handel, P., & Jansson, M. (2003). Effects of frequency and phase errors in electronic warfare TDOA direction-finding systems. In Military Communications Conference, 2003. MILCOM ’03. 2003 IEEE,1(1), 118–123.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uysal, C., Filik, T. A Sparse TDOA Estimation Method for LPI Source Localization Using Distributed Sensors. Wireless Pers Commun 123, 2171–2187 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-09233-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-09233-1