

At first glance, car insurance may seem a straightforward form of cover: it protects you financially if you get into an accident or your vehicle gets stolen. However, this kind of coverage consists of several layers that you must understand to find the best protection possible.
Among these are the different car insurance types. But with the vast number of options available, picking the policies suited to your unique needs can be an overwhelming task.
To make your search for the right coverage easier, Insurance Business lists every type of auto insurance available in the US. We will explain how each one works to help you make an informed decision on which coverages to include in your policy. Read on and learn more about the different car insurance types you can purchase in this guide.
Car insurance companies offer an extensive range of coverage designed to meet the varied needs of each motorist. Some are legally required, depending on the state where you live. Some are optional, depending on your driving record and personal circumstances. And some are unique, catering to very specific needs.
For this guide, we will group the different car insurance types into three categories, which we will discuss in detail in the succeeding sections. These are:
For a quick overview, check out our guide on how car insurance works.
Each state implements different laws when it comes to auto coverage. While the requirements vary, there are certain car insurance types that are mandatory in most states. These are the different forms of coverage commonly included in a standard car insurance policy:
Considered as the foundation of any auto insurance policy, liability car insurance is compulsory in almost all states. It is designed to provide financial protection if you have been found legally responsible (or liable) for an accident that causes injury, death, or property damage to another person.
Liability car insurance comes in two types:
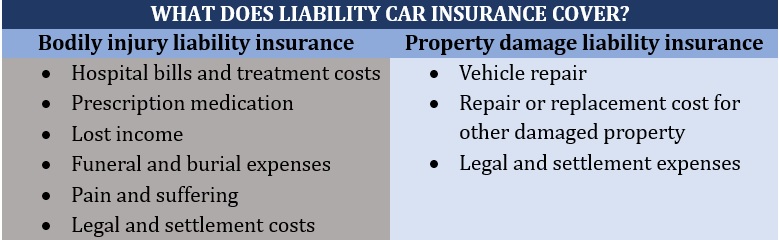
Also referred to as BI coverage, this pays for the medical and treatment expenses another person incurs due to the injuries suffered from an accident you caused. It also covers the legal expenses stemming from a lawsuit, as well as settlement costs. Most policies also pay out for the other driver’s lost wages and funeral expenses.
Bodily injury liability insurance is mandatory in almost all states. In New Hampshire and Virginia, where car insurance is not compulsory, you’re required to have BI coverage if you opt to take out auto insurance. The only exception is Florida. You can find out how coverage works in the state in this guide to car insurance in Florida.
Property damage liability insurance, also called PD coverage, is mandatory in all states if you get car insurance. It compensates another person for the damage and losses they incur because of an accident that you’re responsible for.
A PD policy covers the cost of replacing or repairing the other driver’s vehicle and other damaged property. It also pays for the legal and settlement expenses if you’re slapped with a lawsuit.
The table below details what these two car insurance types commonly cover.
Liability car insurance doesn’t come with a deductible. Under the policy, your auto insurer pays the full cost of the liability claim up to the coverage limits, with the person filing the claim against you receiving compensation.
Personal injury protection coverage, also referred to as PIP, covers the medical and treatment expenses you and your passengers incur because of an accident. Coverage also includes lost wages and the cost of household services if your injury prevents you from performing such tasks. PIP may also offer a death benefit, which can cover funeral and burial expenses.
Personal injury protection insurance applies regardless of who caused the accident. It is mandatory in states that follow no-fault insurance laws, namely:
In these states, you are not allowed to sue an at-fault motorist for compensation. This is unless the injuries you sustain are severe or your medical costs exceed your state’s minimum requirement to sue.
Medical payments coverage or MedPay covers medical and treatment expenses you and your passengers incur in an accident, regardless of who is at fault. It works the same way as PIP coverage but with a few differences. One is that MedPay doesn’t cover lost income. It is also optional in all but two states – Maine and Pennsylvania.
Depending on where you live, MedPay can serve as supplemental coverage for your health insurance or as your primary medical insurance after an accident.
If it’s supplemental, your health coverage will be used first to cover your medical bills while MedPay will cover the deductibles and co-pays.
If MedPay serves as primary coverage, it will pay for your immediate hospital and treatment expenses, while your health policy covers the rest. Unlike your health insurance, however, MedPay doesn’t have a deductible and co-pays.
Also called UM and UIM policies, these car insurance types are often bundled together as they serve the same purpose. Both are designed to fill the gap between the costs you pick up because of an accident and the at-fault driver’s ability to pay.
UM coverage compensates you and your passengers for the injuries and property damage you sustain if you are hit by a driver who doesn’t have coverage. It may also cover hit-and-run incidents.
A UIM policy, meanwhile, provides coverage if the at-fault driver’s insurance is not enough to cover the entire costs.
You can check out which states require these types of car insurance policies in our state-by-state guide to uninsured motorist coverage.
Some car insurance types are optional depending on your personal profile and situation. While the policies listed below are not mandatory, industry experts still recommend that motorists take out these forms of coverage to get full protection. Car dealerships, banks, and other lenders, however, often set these policies as conditions if your vehicle is under lease or financing.
If you take out collision and comprehensive car insurance, along with the state-mandated policies, you are considered to have full coverage. Learn more about full coverage car insurance in this guide.
Some car insurance types cater to specific needs. Many of these policies are automatically included in standard auto insurance or can be added as a rider or endorsement. Some can only be purchased as a standalone policy. Here are the most common add-ons US drivers can access.
An at-fault accident can significantly drive up your premiums. This is where accident forgiveness coverage comes in handy. It helps keep your premiums down by “forgiving” your first at-fault accident. The accident, however, stays on your driving record and can push up your rates if you switch insurers. Accident forgiveness isn’t allowed in California.
This covers the cost of roadside services if your car breaks down or is disabled. Coverage applies if your vehicle needs to be towed, runs out of gas, or has a flat tire. You can also access this benefit if you get locked out of your car or if the battery dies. If you experience any vehicle issues, you will need to inform your insurer, so they can dispatch someone to assist you.
This is often confused with a roadside assistance policy as both car insurance types offer almost the same coverage. The main difference is with towing and labor insurance, you will need to find help yourself.
This optional coverage pays for the repair costs for major mechanical issues not caused by an accident or normal wear and tear. It works just like an extended warranty but is limited to newer vehicles.
This pays an amount equivalent to the value of a brand-new version of your car, instead of the depreciated or actual cash value, if it gets totaled. You can typically purchase new car replacement insurance as an add-on if you have collision and comprehensive coverage. This type of policy comes with a deductible and can’t be combined with gap insurance.
Designed to keep you on the road, this policy pays for the cost to hire a replacement car while your vehicle is being repaired after an accident. This type of coverage is typically not included in a standard auto policy and can be purchased as an add-on.
This form of coverage is often confused with rental car reimbursement insurance because of the name. A rental car policy consists of different car insurance types designed to protect rental or leased vehicles. You can find out more about this kind of coverage in our guide to leased car insurance.
This covers you and your vehicle if you offer ridesharing services. It helps fill the coverage gap between your personal car insurance and the commercial coverage provided by your ridesharing company.
Also called disappearing or vanishing deductible, this is an additional coverage that rewards safe driving practices. This benefit decreases your deductible amount for every year that you maintain a clean driving record and avoid filing claims.
This is designed to align your insurance rates with your driving behavior. It works by adopting onboard technology or mobile applications, called telematics, to monitor your driving habits. This type of car insurance rewards safe driving practices in the form of discounted premiums.
This works similarly to usage-based insurance, with the pricing arrangement based on your mileage instead of driving behavior. The less you drive, the lower your premiums.
This covers aftermarket modifications designed to enhance your vehicle’s appearance or performance. Also called CPE, this policy comes in the form of an endorsement typically added to your collision and comprehensive coverage.
This type of endorsement ensures that only original factory equipment designed for the specific make and model of your car will be used during repairs.
This covers the cost of repairing or replacing your damaged windshield. Some auto insurers call it full auto glass insurance or windshield repair coverage. This is among the car insurance types that commonly doesn’t have a deductible.
Also called excess liability coverage, this policy provides an extra layer of financial protection by covering losses that exceed your coverage limits. This serves to complement your liability car insurance.
This covers the cost to repair or restore a vintage, antique, or classic vehicle if it has been damaged by a covered event. Unlike a standard policy, which typically pays out the actual cash value, classic car insurance covers vehicles based on an agreed cash value basis. This is the amount that you and your insurer have agreed upon following an appraisal.
This works similarly to private auto insurance, but with one major difference: it covers mainly company cars and commercial trucks and vans. It is also among the most essential types of business insurance.
As the name suggests, this is a type of endorsement added to your car insurance policy to extend coverage to miscellaneous vehicles. These include motorcycles, recreational vehicles, motor homes, and motorized golf carts.
This covers veterinary expenses if your pet is injured in a vehicular accident. It also covers burial costs if your pet dies and reimburses the cost of getting a new pet.
The Insurance Information Institute (Triple-I) suggests looking at three major factors to find the auto insurance policy that best fits your needs:
The US is home to thousands of auto insurance providers but only a few dominate the market. If you want to learn more about the industry’s top players, you can check out our rankings of the 10 largest car insurance companies in the US.
Which of the car insurance types listed above do you think are the most essential? Which ones are unnecessary? Feel free to share your thoughts below.
