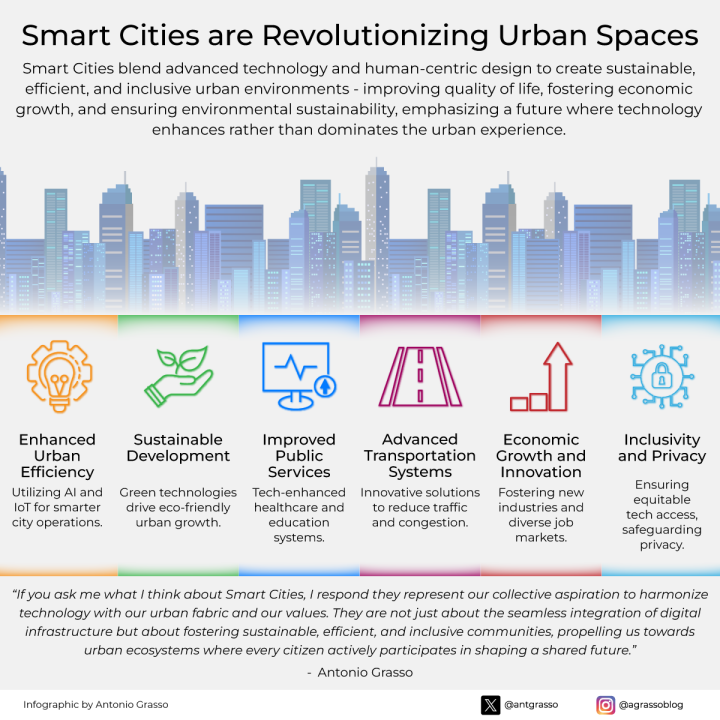
Smart Cities as the New Technological Revolution in Urban Spaces
I firmly believe that the cities of the future stand as prime examples of how technology can transform society and the economy by focusing on people and their needs. This conviction inspired me to write an article about the impending technological revolution awaiting us as global citizens. It was with this mindset that I embarked on my research journey.
While conducting the research, I discovered a profound connection with the mythological figure of Janus, the Roman god of passages, doors, and, in a broader sense, change and transitions. In mythology, Janus is unique for his two-faced appearance, gazing simultaneously into the past and the future. This dual perspective is emblematic of how Smart Cities act as a bridge between the historical legacy of our cities and their future technological prospects.

Janus symbolizes not just the physical passage from one space to another but also the more profound concept of transitioning between different phases and ideas. This symbolism aligns perfectly with the essence of Smart Cities, which embrace a holistic approach to urban modernization: honoring and integrating historical and cultural foundations while boldly projecting toward innovation and sustainability. Just as Janus contemplates two different worlds, Smart Cities harmonize the rich heritage of the past with the promises of an advanced technological future.
These future cities represent the culmination of Janus's two-faced vision: they are forward-thinking urban areas integrating various electronic and digital technologies to collect data. This data is then used to efficiently manage resources, services, and infrastructure, enhancing the quality and performance of urban services such as transportation and utilities, thereby reducing resource consumption, waste, and overall costs.
The evolution of Smart Cities is grounded in the use of ICT (Information and Communication Technologies) to optimize municipal operations and services and to connect with citizens. Technology plays a pivotal role in the development of these cities, acting as the backbone that supports a complex network of services and systems within the urban area. Integrating technology in urban development includes implementing IoT devices, AI, big data analytics, cloud computing, and more. These technologies collaborate to create a more interconnected and efficient urban environment.
As we progress into the 21st century, approaching what I envision as a Post-Digital Society, the role of technology in shaping our urban landscapes becomes increasingly significant, promising a future where urban life is more efficient and more in harmony with its inhabitants and the environment. This vision, reflecting Janus's dualistic aspect, captures the transformation of Smart Cities - a transformation that merges the wisdom of the past with the innovations of the future, shaping spaces that are not only more efficient and sustainable but also more connected and inclusive for everyone who calls them home.
After this premise, drawing inspiration from the duality of Janus and the profound integration of technology in urban development, we now transition to an extensive discussion on the technological aspects. This will explore how various innovative technologies are employed within Smart Cities to reshape and enhance every facet of urban life.
Let me remind you that themes presented here are also explored in depth in my new book, "Toward a Post-Digital Society: Where Digital Evolution Meets People's Revolution," where I dissect the future evolutions of digital technologies, offering insights and broad perspectives. Here is the link to Amazon US > https://amzn.to/47UXxNT. But you can find it on any Amazon international website worldwide or in selected bookstores.
Thank you, and have a great read.

Core Technologies in Smart Cities
Every Smart City relies on a suite of core technologies, each playing a crucial role in reshaping urban environments into more efficient, sustainable, and livable spaces. These technologies serve as the building blocks for modern urban development, seamlessly transforming how cities function and residents interact with their urban surroundings. In this section, I delve into the key technologies fundamental to the Smart City concept, exploring how each contributes uniquely to the city's overall intelligence and efficiency.
AI and Big Data - A Powerful Duo Reshaping Urban Management
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Big Data are revolutionizing the management of urban areas. When combined with the vast amounts of data collected from various city sensors and devices, AI algorithms enable smarter decision-making processes. These technologies are instrumental in analyzing traffic patterns for optimizing road usage, predicting utility demand to manage resources like water and electricity better, and even assisting in public safety by identifying potential high-risk areas.
AI-driven analytics also play a crucial role in urban planning, helping city planners understand population growth patterns, environmental impacts, and infrastructure needs. However, implementing AI and Big Data must be handled with care, ensuring that ethical considerations such as privacy and fairness are addressed.
Internet of Things (IoT) - The Invisible Infrastructure
The Internet of Things (IoT) forms the backbone of the Smart City’s infrastructure, allowing for the interconnection of physical devices like sensors, vehicles, home appliances, and other items embedded with electronics, software, and network connectivity. These IoT devices collect and exchange data, making real-time monitoring and management of city assets possible, leading to more efficient urban operations, such as optimized energy distribution, real-time public transportation updates, and improved emergency response times. IoT helps create a network of intelligent systems that make city life more responsive and convenient.
Cloud Computing is the brain behind Smart City Operations
Cloud computing serves as the central nervous system of Smart Cities, offering powerful data processing capabilities and storage solutions. It enables the vast amount of data generated by a Smart City to be stored, analyzed, and managed efficiently. This technology provides the computing power to process data from IoT devices and AI applications.
Cloud platforms facilitate integrating city services, allowing seamless data sharing and collaboration across different city departments and services. This results in more coordinated urban management and better service delivery to citizens.
Smart Lighting and Energy Management Toward More Sustainable Consumption
Smart lighting and energy management are vital aspects of a sustainable Smart City. Advanced lighting technologies, such as LED lights and automated controls, significantly reduce energy consumption and costs. Smart lighting systems can adjust brightness based on the time of day or the presence of people, further enhancing energy savings.
In the broader context of energy management, Smart Cities use technology to optimize energy generation, distribution, and consumption. This includes integrating renewable energy sources and implementing smart grids that can more efficiently manage and distribute electricity, reducing the city’s carbon footprint and promoting a more sustainable and environmentally friendly urban environment.
Transforming Urban Living through Healthcare, Sustainability, Connectivity, and Transportation in Smart Cities
Smart Cities are leading a revolution, profoundly transforming urban living across multiple fronts with a journey marked by significant advancements in healthcare, a dedicated commitment to environmental sustainability, enhanced social connectivity, and the development of innovative transportation solutions. Through the lens of cutting-edge technology, these pivotal aspects are being redefined, impacting not only the physical infrastructure of cities but also profoundly influencing the daily experiences of their inhabitants.
In the healthcare sector, the integration of technological innovations is revolutionizing medical services, making healthcare more accessible and efficient, thereby significantly improving the quality of life in urban areas. Technological advancements in healthcare are radically transforming the landscape, from how medical services are delivered to how they are received by city residents.
Simultaneously, Smart Cities are reimagining environmental sustainability through intelligent solutions, addressing urgent needs for conservation and responsible resource management. In social connectivity, digital platforms bridge gaps between people and government, fostering community engagement and participatory governance. This is complemented by a redefinition of urban mobility, where technological evolution is making transportation more efficient, eco-friendly, and centered around the user's needs.
As we delve deeper into this chapter, we will explore the key technological advancements shaping urban healthcare, understanding how these innovations transform medical services.
Remote Patient Monitoring Systems
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) systems have emerged as a cornerstone in modern healthcare by harnessing digital technologies to collect medical and health data from patients remotely, typically through wearable devices or home monitoring equipment. Data is then transmitted to healthcare providers for assessment, allowing for continuous monitoring of patients outside traditional clinical settings.
RPM is especially beneficial for managing chronic conditions, post-operative care, and elderly care. It enables early detection of complications, reduces the need for hospital readmissions, and allows patients to receive high-quality care from the comfort of their homes, easing the burden on urban healthcare facilities and enhancing patient engagement and self-management of health.
Telemedicine in Urban Healthcare
Telemedicine has revolutionized how healthcare is delivered via telecommunications technology to provide clinical healthcare from a distance - including consultations via video calls, remote diagnostics, and e-prescriptions. It makes healthcare more accessible, especially for residents in underserved or densely populated areas. It reduces the need for physical travel, saves time, and decreases the pressure on healthcare facilities.
Telemedicine is also critical in providing uninterrupted healthcare services during public health crises, such as pandemics, while minimizing the risk of spreading infections.
Impact of Technology on Healthcare Accessibility and Efficiency
Incorporating technology in urban healthcare has significantly improved accessibility and efficiency. Digital health records, AI-powered diagnostic tools, and e-health applications streamline healthcare processes, reduce administrative burdens, and provide more accurate and timely care.
Technology also bridges the gap for populations with limited access to healthcare facilities, including older adults, people with disabilities, and those living in remote areas. It empowers citizens with better access to health information and resources, leading to more informed health decisions and improved overall health outcomes.
Environmental Sustainability and Smart Cities
Environmental sustainability is a cornerstone in developing Smart Cities, with a dedicated focus on leveraging technology to minimize environmental impact and foster a healthier urban ecosystem.
In this section, we will explore existing strategies like energy conservation, water and waste management, and air quality monitoring and introduce additional examples showcasing how Smart Cities are employing technology to further their sustainability goals.
Building Automation Systems for Energy Conservation
The implementation of building automation systems is pivotal in enhancing sustainability. Beyond integrating sensors and controllers for optimizing heating, ventilation, air conditioning, lighting, and security, these systems are increasingly adopting advanced technologies like AI-driven predictive maintenance. This allows for anticipating system failures or inefficiencies, reducing unnecessary energy use, and prolonging the lifespan of building infrastructure.
Additionally, Smart Cities are exploring smart windows that adjust their transparency based on sunlight intensity, further contributing to energy efficiency by regulating indoor temperatures more naturally and reducing the reliance on heating and cooling systems.
Water Consumption Tracking and Waste Management
In water management - beyond monitoring usage and detecting leaks - Smart Cities are implementing rainwater harvesting systems integrated with IoT technologies. These systems collect and purify rainwater for non-potable uses like irrigation and flushing toilets, significantly reducing the demand for municipal water supply.
For waste management, Smart Cities are advancing towards zero-waste goals by implementing smart recycling bins that monitor fill levels and sort recyclables using image recognition technologies. This enhances the efficiency of recycling processes and encourages responsible waste disposal among residents.
Air Quality Monitoring and Management
In addition to monitoring traditional pollutants, smart cities also track greenhouse gasses like CO2 and methane using advanced sensor networks. This data aids in formulating targeted strategies to reduce the city's carbon footprint.
Urban greenery is being optimized through technology. Smart urban forests and gardens equipped with sensors actively monitor and improve air quality. These green spaces are strategically placed based on environmental data to maximize their impact on air purification and urban cooling, contributing to overall urban health and aesthetics.
Energy Communities
The concept of Energy Communities is a pivotal addition to environmental sustainability in Smart Cities. These collaborative networks enable residents and local businesses to participate actively in energy generation and management.
By employing smart grids, these communities can distribute energy efficiently, reduce costs, and even contribute surplus energy back to the main grid.
Adopting blockchain technology in these communities ensures transparent and secure energy transactions, further empowering residents and fostering a sense of ownership and responsibility towards sustainable energy usage.
Innovative Environmental Practices in Smart Cities
Smart Cities are not just about integrating existing technologies but also hotbeds for experimentation with groundbreaking practices. A prime example of this innovation is the development of energy-generating pavements. These pavements are designed to capture the kinetic energy from pedestrian foot traffic and convert it into electrical energy, harnessing the power of the thousands of daily steps across city streets and turning ordinary walkways into renewable energy sources. Such pavements can power streetlights and digital signage and contribute to the city's electrical grid, exemplifying an innovative approach to sustainable urban energy harvesting.
In addition to these kinetic energy pavements, Smart Cities are transforming their infrastructure to support the growing demand for electric vehicles (EVs). An ingenious solution being adopted is the installation of smart streetlights that serve a dual purpose by providing illumination and charging EVs. This dual-functionality approach simultaneously tackles two challenges: expanding the EV charging station network and upgrading urban lighting systems. By embedding charging stations within streetlights, cities can efficiently utilize existing infrastructure, reducing the need for additional construction and saving on space in densely populated urban areas.
These smart streetlights often incorporate other features such as environmental sensors, Wi-Fi hotspots, and emergency response systems, making them multipurpose assets in the urban landscape. IoT technology enables these streetlights to optimize energy usage, adjust lighting based on real-time conditions, and report malfunctions automatically, further enhancing their efficiency and functionality.
Social Connectivity and Civic Engagement
Social connectivity and civic engagement are vital components of smart cities, fostering a sense of community and enabling residents to participate actively in the governance and improvement of their urban environments. This section explores how digital platforms enhance community interaction, improve communication between residents and local governments, and provide real-world examples of civic participation in Smart Cities.
Digital Platforms for Community Interaction
Digital platforms are revolutionizing community interaction in Smart Cities, serving as virtual town squares where residents can discuss, share information, and collaborate on community projects.
Social media, city-specific apps, and online forums allow for real-time communication and exchange of ideas among community members, permitting virtual town hall meetings to invite residents to participate in civic discussions and voice their opinions on local matters.
By facilitating a more connected community, these digital platforms help to strengthen social bonds and foster a more inclusive and engaged urban society.
Enhancing Communication Between Residents and Local Governments
Effective communication between residents and local governments is essential for responsive and transparent governance. Smart Cities leverage technology to bridge the communication gap between these two entities. Online portals and mobile applications enable residents to report issues, request services, and access important information about city operations.
These technologies also allow local governments to disseminate timely updates, emergency alerts, and policy changes directly to residents. By providing a two-way communication channel, these tools enhance the responsiveness of local governments to citizen needs and increase the accountability and transparency of municipal operations.
Case Studies of Civic Participation in Smart Cities
Smart Cities worldwide provide inspiring examples of how technology can facilitate civic participation. For instance, some cities have implemented participatory budgeting platforms where residents can propose and vote on projects for city funding. Others have developed apps that allow citizens to participate in urban planning initiatives, such as suggesting locations for new public amenities or voting on design proposals.
These case studies demonstrate how technology empowers residents to actively shape their urban environments, leading to more democratic and community-driven city development.
Transforming Urban Transportation
Urban mobility is undergoing a radical transformation, driven by the advent of autonomous public transit, the integration of IoT in vehicles, and the implementation of advanced traffic management systems.
In this section, I delve into how these innovative technologies reshape how we navigate our cities. I explore the emergence of driverless buses and shuttles equipped with cutting-edge navigation and safety technologies - set to revolutionize public transport by optimizing routes, reducing wait times, and enhancing passenger safety.
Alongside this, the integration of IoT in vehicles is playing a crucial role in reducing emissions and streamlining traffic flow, while the incorporation of drone technology in traffic management provides unprecedented insights into urban transit patterns.
Autonomous Public Transit and IoT-Connected Vehicles
Autonomous public transit is swiftly becoming a key player in transforming urban transportation. Cities are experimenting with driverless buses and shuttles equipped with advanced navigation and safety technologies. These vehicles, utilizing state-of-the-art systems like LiDAR and machine learning algorithms, are designed to expertly navigate complex urban environments and adapt to changing traffic conditions, ensuring a high level of passenger safety.
These autonomous vehicles are seamlessly integrated into the broader Smart City infrastructure. They communicate with smart traffic signals and other IoT-enabled elements, enhancing route optimization and reducing wait times for a more efficient public transport experience. This synchronization improves transit efficiency and aligns with environmental sustainability goals. Most autonomous vehicles are electric or hybrid, significantly lowering urban carbon emissions. Moreover, they are crafted to enhance accessibility, focusing on serving underserved communities and providing user-friendly features for passengers with mobility challenges.
Complementing these advancements, Smart Cities further integrate IoT in vehicles to reduce emissions and improve traffic flow. Connected traffic signals interact with cars, optimizing traffic flow and reducing unnecessary stops. This not only curtails fuel consumption but also minimizes emissions. Additionally, implementing innovative parking systems leveraging IoT technology assists drivers in swiftly locating available parking spaces. This reduces the time spent searching for parking and decreases traffic congestion and emissions.
Enhanced Smart Traffic Management Systems with Drone Integration
Integrating drone technology significantly advances how cities handle traffic monitoring and management. These drones, equipped with high-resolution cameras and advanced sensors, offer an unparalleled bird's-eye view of the city's traffic flow, offering a vantage point instrumental in quickly identifying and addressing traffic bottlenecks, road accidents, and other disruptions.
In addition to basic monitoring, drones employ sophisticated analytics to provide real-time data and predictive insights on traffic patterns, proving crucial for traffic authorities in making data-driven decisions to ease congestion, reroute traffic proactively, and improve overall road safety. They can also be equipped with thermal imaging and night vision capabilities, extending their usefulness to 24/7 traffic monitoring, which is particularly beneficial for managing nighttime traffic and responding to incidents outside daylight hours.
The utility of drone technology extends beyond daily traffic control as it is precious in coordinating emergency response efforts. In the event of an accident or a natural disaster, drones can swiftly assess the situation, relay critical information to first responders, and help map out the most efficient routes for emergency services, ensuring a timely and coordinated response.
Drones are becoming indispensable tools for urban planning and development because they can assist in surveying and analyzing traffic impacts for major events, large-scale construction projects, and urban redevelopment plans. By providing a comprehensive overview of how these activities affect traffic flow, city planners can make informed decisions to minimize disruptions and maintain smooth traffic movement.
Advancing Urban Mobility with Multimodal Transportation Platforms
The concept of integrated multimodal transportation platforms is gaining significant momentum in Smart Cities, revolutionizing how citizens navigate urban spaces. These sophisticated platforms amalgamate various modes of transportation, including public transit, micro-mobility options like e-scooters and bikes, ridesharing services, and even car rentals, into one seamless, user-friendly interface, allowing users to effortlessly plan, book, and pay for their journey through a single application, significantly simplifying the travel process.
Beyond basic trip planning, these platforms use advanced algorithms that offer optimized route suggestions based on real-time traffic data, user preferences, and the fastest or most eco-friendly options, ensuring that commuters can make informed decisions about their travel, balancing factors such as time, cost, and environmental impact.
Some of these platforms incorporate dynamic pricing models, which adjust fares based on demand, time of day, and service availability, providing users with more cost-effective travel options and making transportation more affordable. It also helps manage peak-time demand, thereby reducing congestion.
The integration of loyalty and reward programs is another aspect that enhances the appeal of these multimodal platforms. Users can earn points or discounts for eco-friendly transportation options or combine multiple transit modes in a single trip. This not only incentivizes sustainable travel habits but also fosters a sense of community and participation among users.
To further aid accessibility, these platforms often feature multi-language support and are designed to be inclusive for people with disabilities, offering features such as voice commands, screen readers, and accessible route options.
These integrated platforms can interface with city infrastructure, for example, linking with smart parking systems to guide users to available parking spaces or integrating with city event schedules to help users plan their travel around major events.
Economic Implications of Smart City Technologies
Implementing Smart City technologies not only brings about improvements in urban living but also has significant economic implications. This section discusses the cost savings and operational efficiencies achieved through these technologies, their role in economic growth and job creation, and the importance of balancing investments for equitable development.
Cost Savings and Operational Efficiencies
One of the primary economic benefits of Smart City technologies is the considerable cost savings and enhanced operational efficiencies they offer. By integrating IoT, AI, and other smart solutions, cities can optimize resource use, reduce energy consumption, and lower operating costs.
For instance, smart lighting and energy management systems significantly cut down electricity expenses. Similarly, smart waste management systems can optimize collection routes and frequencies, leading to reduced fuel consumption and operational costs.
These efficiencies save money for city administrations and residents, contributing to an overall more cost-effective urban environment.
Economic Growth and Job Creation through Technological Innovation
The adoption of Smart City technologies acts as a catalyst for economic growth and job creation. By fostering an environment ripe for innovation, these technologies attract investments and encourage establishing new businesses, particularly in the tech sector.
The development and maintenance of smart infrastructure and services create a demand for a skilled workforce, leading to job creation in various fields such as engineering, data analysis, software development, and system maintenance. Moreover, the efficiency and attractiveness of Smart Cities can lure global businesses and startups, further boosting the local economy and job market.
Balancing Investment and Equitable Development
While Smart City technologies offer numerous economic benefits, it is crucial to balance these investments to ensure equitable development by directing resources toward technology and addressing the needs of all city residents, including those in underserved communities.
Equitable development ensures that the benefits of Smart City initiatives, such as improved public services, enhanced connectivity, and economic opportunities, are accessible to everyone. This approach helps bridge the digital divide and ensures that the transformation towards smart urban spaces benefits the entire population, contributing to inclusive and sustainable urban development.
Ethical Considerations and Challenges
Smart Cities are employing AI and surveillance for enhanced urban management, which led us to a point where addressing privacy concerns amidst extensive data collection is vital. In this section, we explore the ethical management of data from sources like surveillance cameras and IoT devices, focusing on protecting citizen privacy while maintaining operational efficiency.
We discuss the implementation of transparent policies, robust cybersecurity, and the empowerment of residents in controlling their data. We also analyze the importance of bridging the digital divide and ensuring inclusivity in Smart Cities, emphasizing sustainable and equitable technological development for a responsible and inclusive urban future.
Addressing Privacy Concerns in AI and Surveillance-Enhanced Smart Cities
As Smart Cities increasingly integrate AI and surveillance technologies for improved management and safety, the resulting privacy concerns are becoming a critical issue. Though beneficial for operational efficiency and public safety, the extensive data collection and analysis pose risks of misuse or unauthorized access to personal information. This data, gathered from surveillance cameras, IoT devices, and many sensors, is invaluable for city administration but necessitates stringent privacy protection measures.
To mitigate these concerns, ethical management and handling of data are imperative. Cities must develop and enforce clear, transparent policies that protect citizen privacy and align with legal and moral standards, establishing strict data collection, storage, usage, and sharing guidelines.
Regular audits are essential to ensure compliance with these policies and to identify any potential privacy breaches or vulnerabilities in the system. These audits should be conducted by independent bodies to ensure objectivity and thoroughness.
Robust cybersecurity measures are another critical component in safeguarding against unauthorized data access and breaches. Cities must invest in advanced security technologies and protocols to protect data from cyber threats. This includes encryption, secure data storage solutions, and continuous monitoring of the data infrastructure for any signs of intrusion.
Empowering residents with control over their data is another crucial step in addressing privacy concerns. Residents should have the right to know what data is being collected about them and how it is being used and be able to opt out of data collection if they choose. Implementing user-friendly interfaces that allow residents to access and manage their personal data can foster trust and transparency between city administrations and citizens.
Cities should engage in open dialogue with residents to understand their concerns and expectations regarding privacy. Public awareness campaigns and educational programs about data privacy can also help build an informed and engaged citizenry.
Bridging the Digital Divide and Ensuring Inclusivity for Sustainable Smart City Development
A paramount challenge in the evolution of Smart Cities is addressing the digital divide, which underscores the gap in access to modern information and communication technology among different population segments. This disparity poses the risk of excluding certain groups from the benefits of urban technological advancements.
Therefore, Smart City initiatives must prioritize making technology accessible and affordable for all, ensuring no one is left behind in the digital age. This inclusivity involves implementing digital literacy programs and developing user-friendly digital services that cater to diverse populations, including older adults and people with disabilities. Achieving this level of inclusivity is essential to ensure the equitable distribution of technology's benefits.
Simultaneously, pursuing long-term sustainability in Smart City technologies demands a holistic approach encompassing environmental, economic, and social aspects. The future viability of these cities hinges on the technologies they adopt today being innovative and sustainable over time. This requires meticulous planning, regular evaluations, and a commitment to continuously update and maintain these technologies, ensuring they remain effective and beneficial as urban needs and circumstances evolve.
Economic sustainability is also crucial. Smart City technologies must offer long-term cost-effectiveness, with efficiency gains, cost savings, and enhanced quality of urban services justifying their investment. This includes considering the total cost of ownership, from installation to maintenance and eventual replacement.
Furthermore, social sustainability, encompassing the inclusivity and accessibility of technology, is vital. Technologies should be designed to serve all urban communities, including the most vulnerable and marginalized, ensuring equitable benefits distribution.
The environmental impact throughout the lifecycle of these technologies is another significant consideration. Cities should adopt responsible practices in material sourcing, energy-efficient operations, and eco-friendly disposal and recycling of outdated technologies. This approach aligns with broader goals of environmental conservation and climate change mitigation.
By integrating circular economy principles into their technological strategies, Smart Cities can minimize waste and maximize resource use and reuse, further promoting sustainability and reducing environmental impact.
Together, these strategies ensure that Smart City development is technologically advanced, innovative, inclusive, economically viable, and environmentally responsible, paving the way for a sustainable and equitable urban future.
Janus Inspires the Future of Sustainable and Inclusive Smart Cities
As we navigate the threshold of a new epoch in urban development, the transformative power of technology in reshaping our cityscapes stands as a testament to our times. This exploration into the essence of Smart Cities has revealed the profound analogy with Janus, the Roman god of transitions.
Like Janus, Smart Cities embody a duality – they are at once a reflection of our historical lineage and a leap into a future where technology harmonizes with human values.
The fusion of advanced technologies like AI, IoT, and cloud computing in urban environments is akin to looking through Janus's dual-faced gaze. On one side, we see our cities' heritage and traditional fabric; on the other, we see a future shaped by smart, responsive, and interconnected technologies.
This duality enhances efficiency and sustainability and fosters a more human-centric urban ethos. Our cities are evolving into entities that should function with precision and care with empathy, embodying the best of both worlds that Janus oversees.
In this technological renaissance, ethical and responsible integration principles are paramount. Our journey toward Smart Cities mirrors the balanced vision of Janus, ensuring that progress does not overshadow our foundational values of privacy, inclusivity, and sustainability.
We must construct urban landscapes that resonate with our shared human values, where technology serves not as an end but as a means to enhance the quality of life for all - Smart Cities that are intelligent in their operations and wise in their understanding and treatment of every citizen.
Looking ahead, the future of Smart Cities is an inspiring blend of human ingenuity, technological advancement, and ethical responsibility. We envision cities that reflect Janus's wisdom in resource utilization, active citizen engagement, and foresight in addressing challenges.
We must be aware that we stand on the cusp of an era where technology empowers us to reach new heights in urban living, bringing us closer to communities that exemplify the pinnacle of human achievement and values.
Let us stride into this future with optimism and clarity. The path ahead shines brightly with the promise of cities that transcend mere living spaces – they are to be cradles of human experience, embodiments of our collective values, and living representations of the magnificent potential inherent in our united endeavors.
The future of Smart Cities lies in building not just better cities but a better world that resonates with Janus's duality and wisdom, echoing our beliefs in an inclusive, ethical, and enlightened urban future.
=====
In thanking you for reading my article, I want to remind you that while this article has delved into the transformation of our cities, it is just a glimpse into the broader discussion of our imminent shift to a post-digital society.
These themes are further explored and integrated into a global context in my new book, 'Toward a Post-Digital Society - Where Digital Evolution Meets People’s Revolution,' available online and in bookstores. Here is the link to Amazon US > https://amzn.to/47UXxNT. But you can find it on any Amazon international website worldwide or in selected bookstores.
Thank you.
Acknowledgments
As we conclude this exploration into the transformative world of Smart Cities, I extend my heartfelt gratitude to the invaluable sources that allowed me to significantly enrich this article.
A special thank you to: McKinsey & Company - Microsoft in Business Blogs - Thales Group - Particle - Rethinking The Future - History Skills.